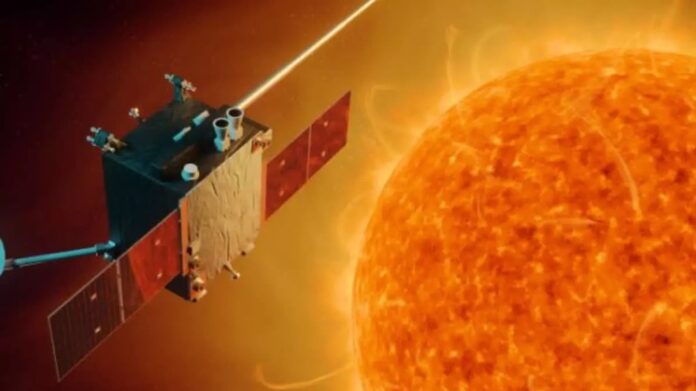
India’s space ambitions soared as the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) Aditya-L1, the nation’s inaugural mission dedicated to studying the Sun, reached its ultimate orbital destination on Saturday. This milestone marks a significant achievement in India’s space odyssey, positioning the nearly 1,500 kg satellite in a space-based observatory approximately 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth.
Costing ₹400 crore, Aditya-L1 is hailed as India’s premier space-based observatory, poised to explore the Sun from a unique vantage point. After commencing its ambitious journey from ISRO’s Sriharikota launchpad over four months ago, the satellite has now reached its intended halo orbit around Lagrange point 1 (L1).
The strategic choice of L1 for Aditya-L1’s final destination holds immense significance. This point offers an advantageous position, providing uninterrupted observations of the Sun without being hindered by eclipses. The satellite’s expected placement at approximately 4 pm on Saturday signifies a crucial maneuver that binds it to the halo orbit around L1, preventing potential deviation toward the Sun.
An ISRO official highlighted the mission’s pivotal role in monitoring space weather and alerting scientists about potentially adverse solar phenomena such as storms and flares, which could impact satellite operations and the broader solar system.
Aditya-L1’s continuous monitoring of the Sun allows for early warnings of electromagnetic disturbances, safeguarding vital assets such as over 50 operational satellites worth ₹50,000 crores. ISRO Chairman S Somanath emphasized the mission’s role in protecting these assets and ensuring their uninterrupted functionality during solar disturbances.
With seven payloads onboard, Aditya-L1 is primed to conduct extensive scientific experiments. It aims to deepen our understanding of the Sun’s various layers, including the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, utilizing electromagnetic, particle, and magnetic field detectors.
The mission’s scientific objectives encompass an array of crucial studies, including solar atmospheric dynamics, coronal heating, plasma physics, coronal mass ejections, and solar wind dynamics, among others.
ISRO underscores the mission’s importance in unraveling the mysteries of space weather and the solar phenomena that impact our planet and technology. Aditya-L1’s groundbreaking observations promise to provide invaluable insights into solar dynamics, contributing to enhanced space weather forecasting and mitigating potential disruptions to satellite operations.
Sources By Agencies